Immune cells are specialized white blood cells (also called leukocytes) that circulate through our blood vessels and settle in many of our tissues and organs. They are on constant watch for anything that appears to be foreign and might be considered a threat to our health.
Immune cells are divided into two main groups—innate immune cells and adaptive immune cells. Within each of these groups are several subsets of cells that have specific jobs. Much like soldiers in a military operation, immune cells use different tactics and communication strategies to overpower the enemy.
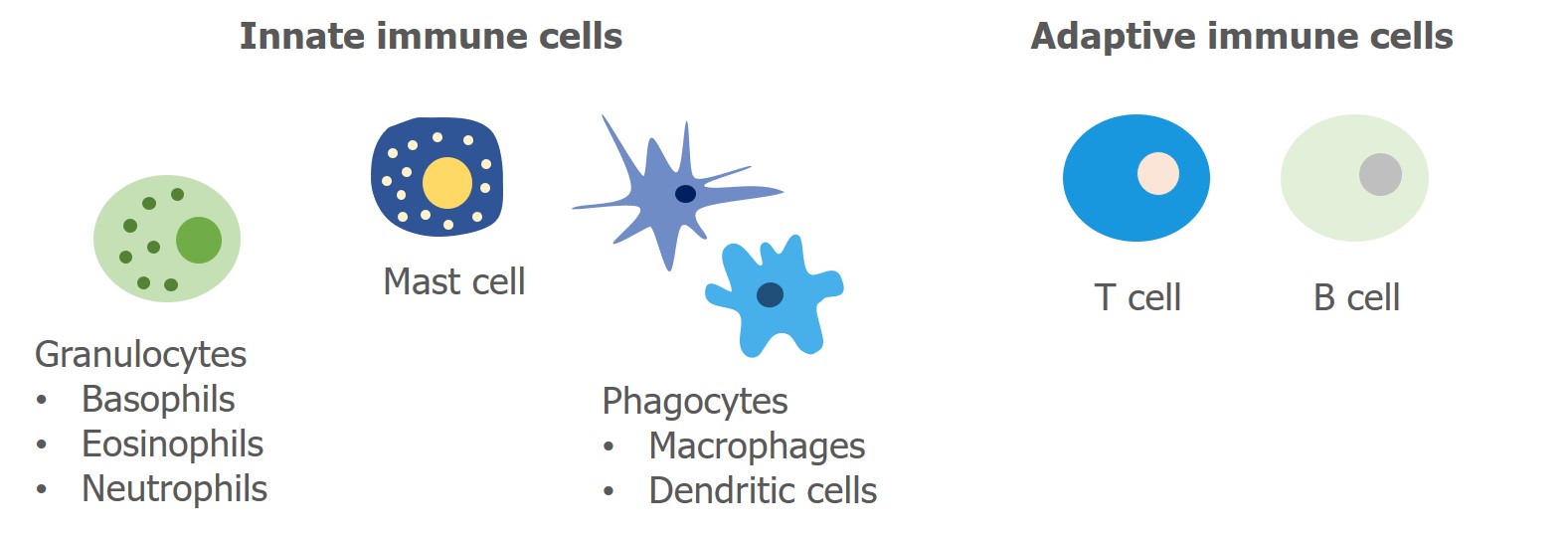
Innate immune cells
Innate immune cells act as the first responders to infection. They attack and eliminate many pathogens using basic methods that are harmful to cells. Different types of immune cells use different techniques. For example, cells called granulocytes (which include basophils, neutrophils, and eosinophils) kill pathogens by releasing toxic molecules. In contrast, other cells called phagocytes (which include macrophages and dendritic cells) ingest—or eat—pathogens to prevent them from causing damage to normal healthy tissues in the body.
Adaptive immune cells
Adaptive immune cells recognize specific pathogens and work together to create a customized immune response. Adaptive immune cells are either T lymphocytes (T cells) or B lymphocytes (B cells). These lymphocytes were named after the place in the body where they mature—T cells mature in the thymus and B cells in the bone marrow. T cells and B cells play major roles in autoimmunity and celiac disease and will be discussed in more detail in later sections.
Glossary
Adaptive immune cells – Immune cells that recognize specific pathogens. Allow the immune system to “remember” pathogens in case of future infection.
B cell – A type of adaptive immune cell. Also called B lymphocyte.
Granulocytes – A type of innate immune cell that releases toxic molecules to fight infection.
Immune cells – Specialized white blood cells (also called leukocytes) that fight infection.
Innate immune cells – Nonspecific immune cells. Recognize many pathogens. First responders to infection.
Leukocytes – Specialized white blood cells (also called immune cells) that fight infection.
Lymphocytes – Adaptive immune cells. Can by B or T lymphocytes.
Pathogen – Bacteria and viruses that can cause disease.
Phagocytes – A type of innate immune cells that ingests (or eats) pathogens.
T cell – A type of adaptive immune cell. Also called T lymphocyte.
Related
Celiac Disease: Biology Basics
May 17, 2018What Happens In the Small Intestine?
May 6, 2018B Cells
May 6, 2018What Role Does Tissue Transglutaminase (tTG) Play in Celiac Disease?
May 6, 2018Share this Post